Ancient Egypt And Nubia Map
Aboriginal Arab republic of egypt had its origin in the course of the Nile River. It reached three periods of keen pharaonic splendor: the Ancient Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom and the New Kingdom.
Ancient Arab republic of egypt map domain stretched from the delta of the Nile in the north, to Elephantine Isle, where is the first cataract of the Nile in the south.
In different periods its expansion reached the eastern desert, the coastline of the Red Ocean and the Sinai Peninsula. Formerly it was divided into Upper and Lower Egypt (southward and north).
This civilisation adult over three,000 years until the year 31 BC the Roman Empire conquered the Ptolemaic Arab republic of egypt that ends up disappearing as a country.
The cultural identity began to be diluted after the conquests of the kings of Babylon and Macedonia. In improver, with the inflow of Christianity, ancient Arab republic of egypt religion disappeared.
The fertile deposits of the Nile River had allowed the Egyptians to practise agriculture in a less laborious way, then that the ancient Egyptians could devote more time to applied science, art and cultural development. The State controlled natural and human resources.
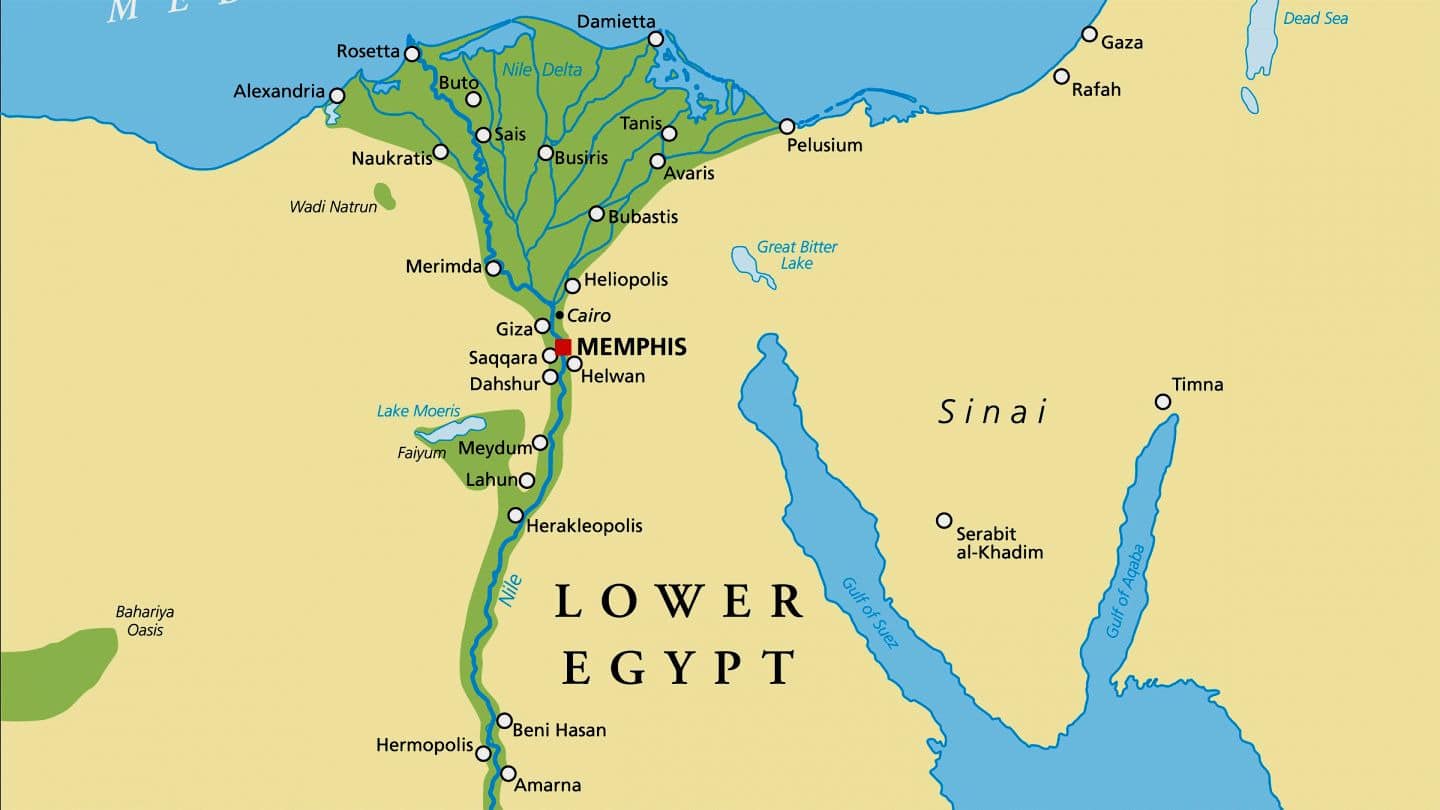
ancient Egypt map "Lower Arab republic of egypt"
i. Ancient Egypt map: Nile delta.
A delta is a betoken in the form of a river where it enters a larger water body. It is named a delta when the river subdivides into numerous tributaries every bit it pours into a larger water torso e.g a lake, body of water or ocean.
The Ancient Nile delta is approximated to be 90 KM in length and 240 KM in width along the coastline. Overtime, people accept been settling effectually the delta for thousands of years due to its rich agricultural soil deposits.
The ancient Nile delta originally had several tributaries, The tributaries of the Nile delta spread out in a Five shape and poured its waters into the Mediterranean sea through the lower part of Egypt.
This area was vastly covered by deposits of silt and was pushed outwards playing a major part in creating an Egyptian boundaries. Nile Delta tributaries were seven in number and spread out from Due east to West.
The lower role of Egypt was mapped by the Nile delta. Aboriginal Egyptians relied heavily on the Nile river for a reliable source of water for both agronomical and besides for the development of commercial settlements.
Despite the floods experienced forth the Nile and its lower parts, the predictability of the Nile waters enabled the Egyptians to program the growth of crops in fourth dimension.
In improver to the Nile being a major source of water, it besides housed fishes and waterfowl.
Furthermore, canoes and boats were used on the Nile for transportation purposes from i end to another.
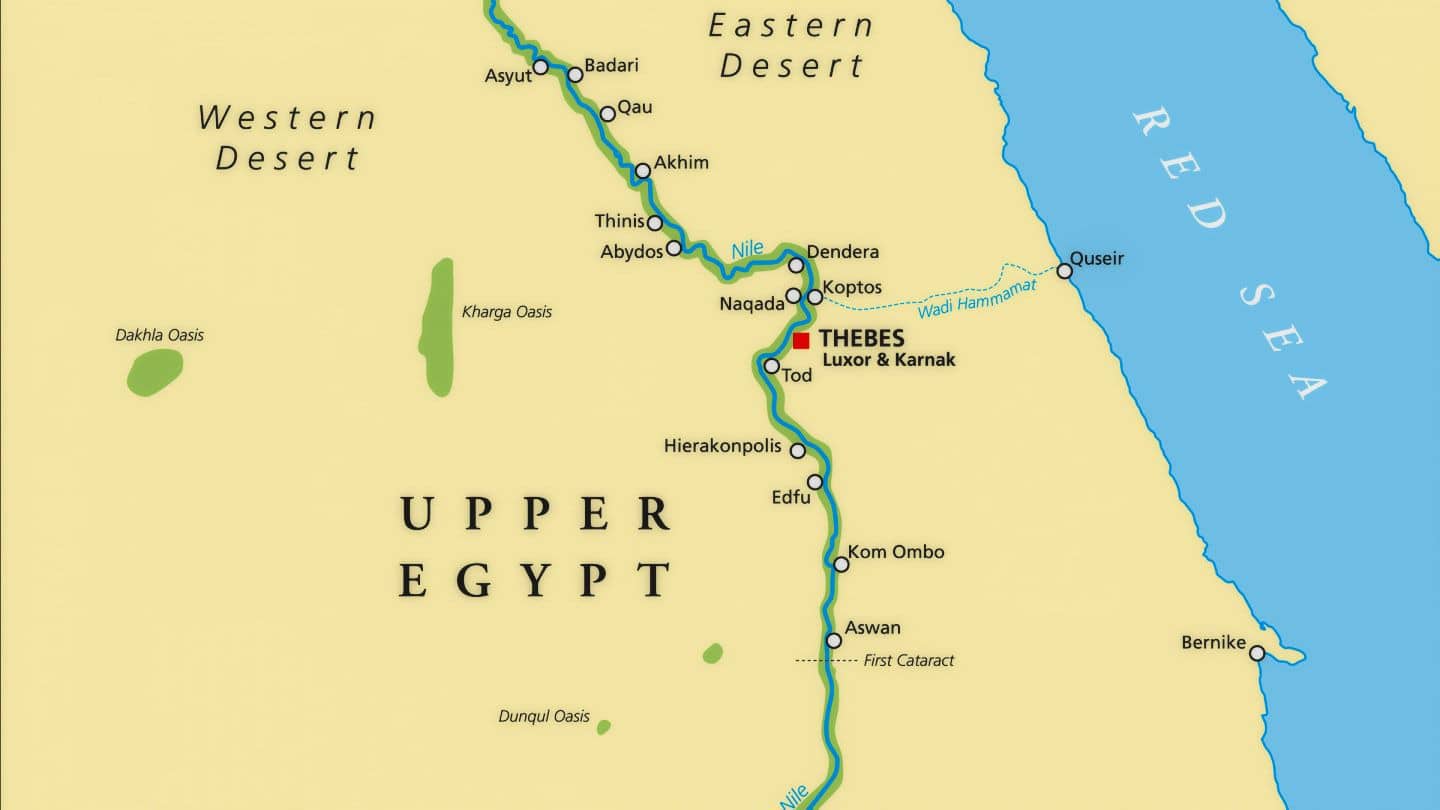
aboriginal Arab republic of egypt map "Upper Arab republic of egypt"
2. Map of aboriginal Egyptian empire.
The Ancient Egyptian empire was formed during the reign of the outset Egyptian King. This catamenia was around 31oo BC and occupied the tip of the Nile delta.
It was at this menstruation when the major uppercase of ancient Arab republic of egypt was formed.
The ancient Egyptian empire survived relative stability despite periods of transition in leadership, the empire was invaded by foreign powers during its period of dull turn down past the command of Alexander the Great.
Greek kingdom ruled Arab republic of egypt for a long flow of fourth dimension until it was taken over by the Romans.
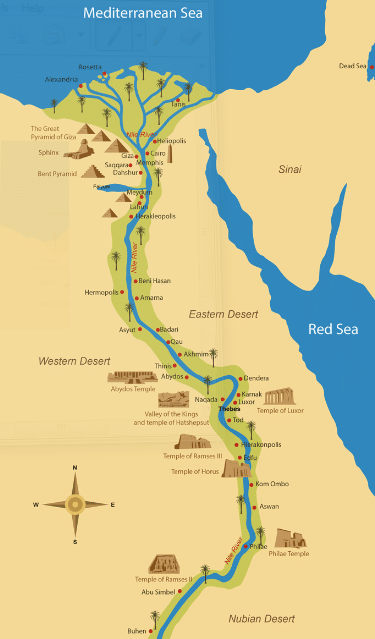
3.Map of aboriginal Egypt and Nubia.
The north of a Nubia creates the boundary of the upper part of Egypt the Nubian and Egyptians had a long term peaceful human relationship mainly because they traded together in commodities such as golden and too engaged in slave trade as a restful of this interaction the people of Egypt conquered the Nubian and thus expanding their territories to the south.
The upper and lower part of Arab republic of egypt were ruled by dissimilar kings up to the time of pharaoh Narmer who unified both upper and lower Arab republic of egypt, Nubia served as a merchandise point between the Egyptians and the people of Nubia as a result of greed for trade Egyptians decided to conquer the Nubian so every bit to command trade boundaries.
Egyptians did this mainly because Nubia was the gateway to learn African richness and every bit they were expanding their territories, they built forts and with this it pb to the Nubians being assimilated by the Egyptians.

Read more: Why exercise Egyptian statues have cleaved noses?

Aboriginal Egypt Maps by Time Periods
Early Dynastic Period 2850-2650
1st Dynasty- 2nd Dynasty
The Leaders
Menes-Narmer/ Hor-Aha/ Uagi/ Den / Seth-Peribsen
Ceremonious events
- Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt. Forming a single kingdom.
- Evolution of the funeral architecture.
- Foundation of Memphis in the boundary between the two parts of the Country.
Military events
- Campaigns against the Nubians
- Extension of the Egyptian territory southward of the first cataract

Ancient Arab republic of egypt Maps. Early on Dynastic Catamenia
Old Kingdom
3rd Dynasty(2650-2600) – 4thursday Dynasty(2600-2480)- 5thursday Dynasty(2480-2350)- sixthursday Dynasty(2350-2190)
The Leaders
Djoser / Sneferu / Khufu / Menkaure / Userkaf / Sahure / Unas/ Pepi I/ Pepi Two
Civil Events
- Construction of the great pyramids
- testimony of a loftier technical
- artistic level and economic prosperity
- Intensification of commercial relations with the Nubians, Libyans and Semites of the Nigh E.
- The first religious texts are written, the Texts of the Pyramids with ritual formulas for the cult of the dead.
- Towards the terminate of the period the autonomy of local authorities and the process of "federalization" of Egypt to the detriment of the authority of the sovereign are accentuated.
Military Events
- Sneferu carries out attacks in Nubia and Libia to fight the invasion and pillage.
- Sahure makes a maritime expedition confronting Byblos.
- During the region of Pepi I the important campaign against the Syrian-Palestinian tribes take identify.

Ancient Egypt Maps. Sometime Kingdom
First Intermediate Menstruation 2190-2050
7th Dynasty (Memphis)- 8th Dynasty (Coptic and Abydos)- 9th Dynasty (Heracleopolis)- 10th Dynasty (Heracleopolis)
The Leaders
Khety I / Khety 3/ Merikare
Civil Events
- Fracture of the unity of the empire and formation of semiautonomous principalities; formation of local dynasties in Memphis, Copts, Abydos; the sovereign of Heracleopolis predominates over all of them.
- Original literary works flourish, for example: Instructions for Male monarch Merikare and dialogue of a man tired of life, with his soul.
Military Events
- Frequent wars between the lords of the various regions (nomos) for achieving supremacy.
- Invasions and incursions from the Nigh East.

Aboriginal Arab republic of egypt Maps. First Intermediate Menstruum
Middle Kingdom 2050-1780
11th Dynasty (2130-1991) – 12th Dynasty (1991-1780)
The Leaders
Mentuhotep I / Amenemhat I/ Sesostris I/ Amenemhat Ii/ Sesostris 2/ Sesostris III/ Amenemhat Iii/ Amenemhat IV
Civil Events
- Reunification of Egypt nether the sovereigns of Thebes.
- The construction of the awe-inspiring tombs begins on the eastern depository financial institution of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor and Karnak).
- The capital is transferred, stationed in Lisht, the administration is reorganized and ability is centralized.
Military Events
- Expeditions of exploration to Sinai and Arabia. Military machine campaign of Sesostris 3 in Palestine.
- Conquest of Nubia by Sesostris III.

Aboriginal Egypt Maps. Center Kingdom
Second Intermediate Period 1780-1560
13th Dynasty (1780-1700) – fourteenthursday Dynasty (1780-1700) – 15th Dynasty (1700-1630) – 16th Dynasty (1630-1580) – 16th Dynasty (1610-1560)
The Leaders
Apepi / Seqenenre Tao 2/ Kamose / Ahmose I
Civil Events
- Repeated dynastic crises and disintegration of central power.
- Decadence and impoverishment of the country.
- Chaotic situation determined by the invasion of the Hyksos "lords of foreign countries".
- Awakening of national sentiment and insurrection against the Hyksos.
Military Events
- Invasions of the Hyksos who conquer Lower Egypt and plant their dynasties there.
- Military campaigns against the Hyksos conducted by Seqenenre Tao II sovereign of Thebes who dies fighting.
- Ahmose conquers the capital of the Hyksos, Avaris, and pursues his adversaries to Palestine.
- Expeditions of Ahmose against Syrian arab republic and Nubia that has returned to get independent.

Ancient Egypt Maps. Second Intermediate Period
New Kingdom 1560-1085
18thursday Dynasty (1560-1345) – xixth Dynasty (1345-1220) – 20thursday Dynasty (1220-1085)
The Leaders
Thutmose I/ Thutmosis 2/ Hatshepsut/ Thutmose III/ Amenhotep II/ Thutmose Four/ Amenhotep Three / Amenhotep 4 (Akhenaten)/ Tutankhamun/ Horemheb/ Seti I / Ramses 2/ Merneptah / Ramses Three
Ceremonious Events
- The construction of the rupestrian or hypogean tombs begins in the Valley of the Kings.
- Alliance with the king of Mitanni concerted past Thutmosis IV.
- Religious reform ordered past Amenhotep Iv (Akhenaten) and centered on the cult of the solar god, Aten, bearer of life.
- Construction of the new majuscule; Akhetaten, opposition of the Theban clergy and failure of the reform.
- Transfer of the capital Pi-Ramesses to the delta by Ramses Ii.
Military Events
- Thutmose I, Nubian reconquest.
- Victory of Thutmose III over the local princes in Megiddo and Palestine: Palestine and Syria become Egyptian provinces.
- During the reign of Akhenaten revolts the Eastward.
- Campaigns of Ramses I and Ramses Ii to conquer Palestine and Syria.
- Boxing of Kadesh of uncertain outcome betwixt the Egyptians of Ramses Ii and the Hittites of Muwatalli. Attempt of invasion of the "People of the Bounding main" repelled by Ramses Ii.

Ancient Egypt Maps. New Kingdom
Third Intermediate Period 1085-715
21st Dynasty (1085-950) – 22nd Dynasty (950-730) – 23rd Dynasty (817-730) – 24th Dynasty (730-715)
The Leaders
Smendes / Herihor/ Sheshonq I/ Tefnakht/ Bakenrenef
Civil Events
- End of the Egyptian unit.
- Multiplying the independent principalities: towards the heart of the eighth century iv local sovereigns claim the championship of Pharaoh.
Military Events
- Nubians from the Kush kingdom invade Upper Egypt.

The Late Menstruum 715-332
25thursday Dynasty (750-656) – 26th Dynasty (663-525) – 27th Dynasty (525-404) – 28thursday Dynasty (404-398) – 29th Dynasty (398-378) – 30th Dynasty (378-341) – 31st Dynasty (341-332)
The Leaders
Piye / Sabacom/ Tantamani / Psamtik I / Necho / Psamtik Two/ Amasis/ Psamtik III/ Amirteo/ Nectanebo Two
Civil Events
- Egypt, reunified past the sovereigns of Sais, after the Assyrian domination, experiences an economic renaissance (saita rebirth).
- The construction of a canal between the Nile and Carmine Body of water begins during the reign of Pharaoh Necho.
- Phoenician sailors travel effectually Africa on account and order of Necho.
Military Events
- The sovereigns of Kush conquer all Arab republic of egypt and unite Nubia and Egypt in a single kingdom.
- Invasion of the Assyrians and their domination in Arab republic of egypt.
- Rebellion of Psamtik, prince of Sais, that frees the country from the Assyrians.
- In Pelusio on the delta, Psamtik III is defeated by the Persians, who organize Egypt every bit a satrapy of his empire.
- The princes of Sais, Mendes and Benito make the last and ephemeral attempts to liberate Egypt from the Persians.

merrittcartographic.co.united kingdom of great britain and northern ireland/ store
Political Organisation in Ancient Egypt
The ancient Egyptian government was characterized past being monarchical, absolutism and theocratic.
The Pharaoh
The government was in the hands of a person chosen Pharaoh, who lived surrounded by a bully court of privileged nobles, officials, priests and warriors.
Pharaoh was the master of all men, possessor of all lands and all waters of the Nile. His will was constabulary.
The pharaoh was considered the son of the god Ra (Lord's day), who had given him power to rule men.
Therefore mortals owed him corking reverence and none of them could pronounce his name without calculation the following expression :> that life and health flourish in him.
Auxiliary Officials in the Regime
Many government functions were delegated to people pharaoh tin trust, who provided constructive collaboration. Among the master officials:
The Majestic Scribe, who was charged with keeping track of agronomical income and inspecting industries and commerce. For this they had to exist experts in the handling of numbers and writing.
The Great Vizier, in charge of controlling the provinces, was the intermediary betwixt the authorities and the pharaoh.
The Caput of the Country Seal, currently compared to the Ministry building of Economic system, whose function was to monitor the taxation revenues and expenses of the Land
The Slap-up Priest, who was in accuse of religious worship and was concerned with presenting the pharaohs equally descendants of the gods.
Writing in Ancient Egypt
The aboriginal Egyptians wrote with small pointed reeds, dipped in a kind of ink, prepared with water, rubber and plant substances.
They used as paper the papyrus stalks, which grew on the banks of the Nile River.
The Egyptian writing script was deciphered past the Frenchman Jean-François Champollion in 1822.
The central was provided by the discovery of the Rosette Rock in 1799, by the soldier Pierre-François Bouchard, when Napoleon Bonaparte made the expedition to the land of the Nile.
Hieroglyphic writing was a difficult interpretation, as it was formed past signs and images of animals and objects. Information technology was mostly used in tombs and temples.
Hieratic Writing is the same hieroglyphic writing but in abbreviated course. Its use was limited to priests and people of great culture.
Demotic Writing is simplified hieratic writing. Information technology was used past the townspeople.
Read More: Photos of lavish pieces of aboriginal Egyptian jewelry

Ancient Egypt Maps

Source:
Amigos de la Egiptologia
Ancient Egypt And Nubia Map,
Source: https://historicaleve.com/ancient-egypt-map/
Posted by: weatherlydepeonew1989.blogspot.com



0 Response to "Ancient Egypt And Nubia Map"
Post a Comment